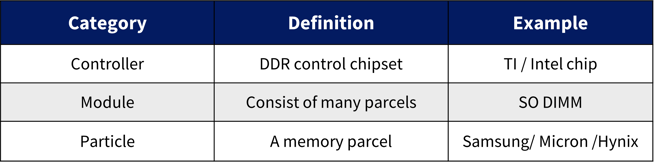
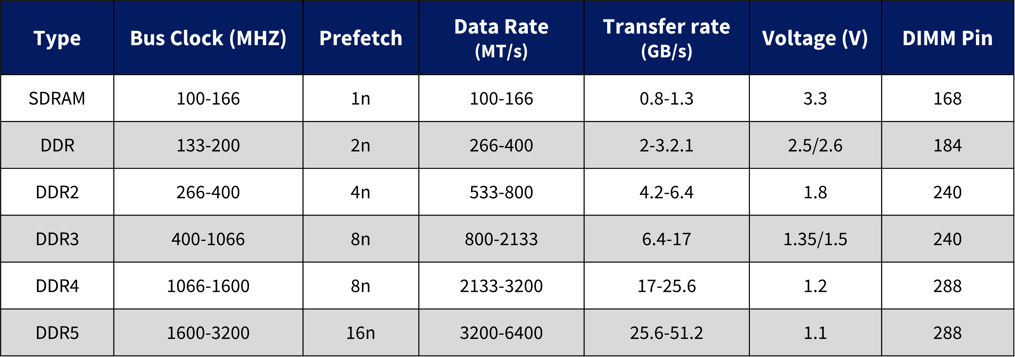
An interposer must be installed at the DRAM component to probe the DDR signals. The interposer may be de-embedded if s-parameters are available. GRL can select and install DDR interposers (billed at cost).
Customer needs to provide:
- Exact DQ (data bit), DQS (strobe), and A (address bit) for each part to be tested.
- Host controller system
- Software tool to generate specific traffic that targets the chip where the DDR interposer is installed to exercise the DQ and Address bits as much as possible for the duration of the test.
The DDR traffic requirements are:
- DDR Writes only with random data and burst of no less than 8-words. The data is required to be random to get as many ‘b0 and ‘b1 as possible in burst transaction for the application to build a DDR Eye. DDR5 requires at least 200 CK cycles for any traffic generation.
- DDR Reads only with random data and burst of no less than 8-words. The script could have a random write performed to a designated location and then start infinite burst reads.
- DDR Write/Read bursts in alternative mode is the best traffic to be used for testing against JEDEC Specification