Under Mandatory Testing Certification of Telecommunication Equipment (MTCTE) regulations, any original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or importer who wishes to sell, import, or use telecom equipment in India must be compliant to the Telecommunication Engineering Center (TEC) standards. The testing required for certification aims to ensure that the equipment meets relevant national and international standards. This encompasses verifying its safety, ensuring radio frequency emissions are within prescribed limits, confirming it does not degrade network performance, and ensuring compliance with national security requirements.
The Testing and Certification framework requires that all telecom equipment entering India meets the essential requirements under:
(a) EMI/EMC
(b) Safety
(c) Technical requirements
(d) Other requirements and
(e) Cybersecurity requirements
Role of NCCS
The NCCS is responsible for setting the security requirements under the 'Communication Security Certification Scheme' (ComSeC) scheme, which is mandated by the MTCTE for the security certification of all telecommunication equipment. It comprises of three major activities:
- Development of country specific security assurance standards called Indian Telecom Security Assurance Requirements (ITSARs) for every telecom equipment
- Designation of third-party Telecom Security Test Laboratories (TSTL) that meet specified requirements. The designated TSTLs will be responsible for carrying out the security testing of telecom equipment in accordance with ITSAR’s requirements
- Evaluation and certification of telecom equipment against the ITSARs by NCCS
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) aims to meet the following objectives in developing, operating and maintaining the ComSec scheme:
-
To develop country specific standards, processes and specifications.
-
To develop a testing and certification ecosystem.
-
To ensure telecom network elements meet security assurance requirements.
-
To ensure compliance of regulatory requirements pertaining to security testing.
Indian Telecom Security Assurance Requirements (ITSARs)
Indian Telecom Security Assurance Requirements (ITSAR) is a set of security guidelines and standards established by the NCCS. ITSAR ensures the security and integrity of telecom networks in India and is applicable to all telecom service providers in India. Areas covered by ITSAR include network security, data privacy, and lawful interception.
The implementation of ITSAR has become imperative for several reasons.
First, it plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and resilience of telecom networks in India, safeguarding them against cyber attacks, data breaches, and other security threats. This is of utmost importance due to the growing dependence on telecom networks for critical services like banking, healthcare, transportation, and more.
The ITSARs are referenced in accordance with TSDSI 3GPP, broadly covering the following technical requirements:
- Access and Authorization
- Authentication Attribute Management
- Software Security
- System Secure Execution Environment
- User Audit
- Data Protection
- Network Services
- Attack Prevention Mechanisms
- Vulnerability Testing Requirements
- Operating System
- Web Servers
- Other Security Requirements
ITSAR also helps to promote trust and confidence in India's telecom sector by ensuring that telecom service providers adhere to strict security standards and guidelines. This, in turn, can help to attract investment and spur innovation in the sector.
Finally, ITSAR is an important tool for the Indian government in its efforts to combat terrorism and other forms of criminal activity. The guidelines and standards established under ITSAR provide the government with the means to monitor and intercept telecom communications when necessary, while also ensuring that the privacy and rights of citizens are protected.
NCCS is responsible for the development and release of ITSARs for various equipment in a phased manner. When an equipment's ITSAR is released, it is included in the Scheme for enforcement. The ITSAR for that equipment becomes effective from the separately notified date. Any amendments made to address emerging threats and requirements will result in a new version of ITSAR, which will be applicable from the indicated date of applicability in the new version.
ITSARs are prepared based on country-specific security requirements, international standards, and consultations with various stakeholders such as OEMs, TSTLs, TSPs, academic institutes, industry and government bodies.
The security testing against ITSAR shall be carried out by the designated TSTL. Applicants intending to get their equipment certified will register on MTCTE. After successful evaluation of the Application, the applicant can choose a designated TSTL for security testing of its equipment against the applicable ITSAR. TSTL will conduct the requisite testing under the supervision of a validator. After completion of the testing, test reports will be submitted by the TSTL. These reports will be evaluated for security certification. Upon successful evaluation, a security certificate will be issued by NCCS.
Procedure to Security Certification
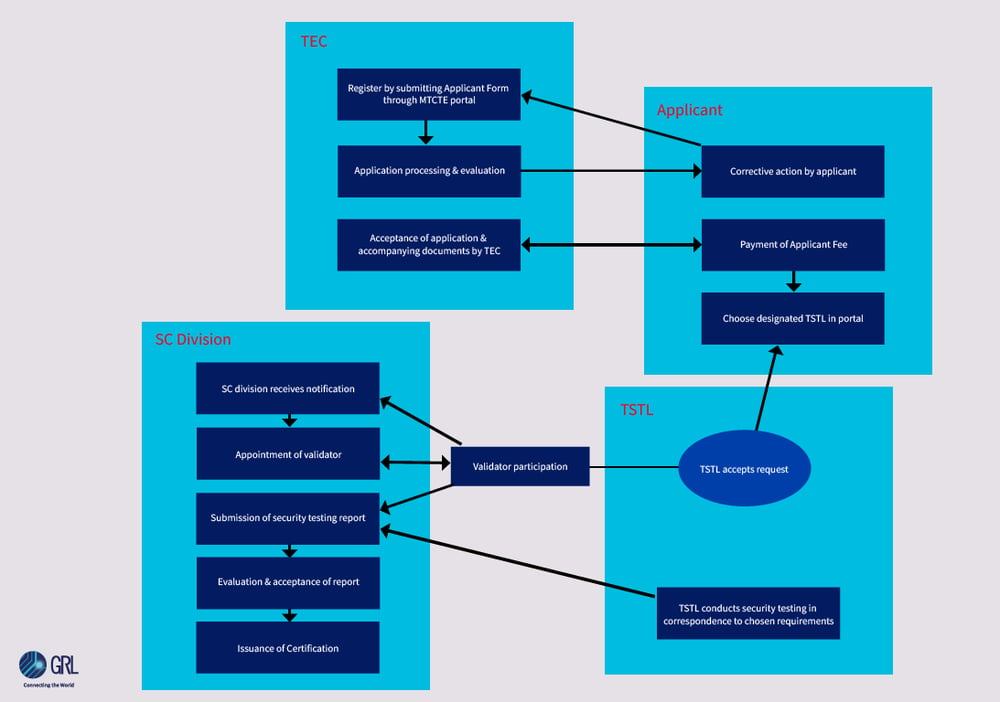
(Zoom in or open image in new tab for details)
The Security Certification process broadly consists of two parts;
1. Testing against applicable ITSARs
2. Evaluation of test results to ensure conformance with requirements.
If equipment is found compliant with all applicable ITSARs, it will be certified to that effect.
Any applicant seeking certification under this scheme may apply online on MTCTE portal. The applicant may provide relevant documents, such as:
(i) Company Registration
(ii) Letter issued by the company authorizing the applicant for related responsibilities.
Additionally, in case of foreign OEMs, the applicant from Indian company shall provide
documents in support of
(iii) MoU between foreign OEM and Indian representative (AIR) for sale and support of the product in India, and
(iv) authorizing the AIR for MTCTE related responsibilities.
The documents will be carefully examined, and any discrepancies will be communicated to the applicant.
The applicant's documents will undergo a thorough examination, and if any inconsistencies are found, they will be notified. Once the necessary corrections are made, the applicant's registration will be approved.
The applicant is required to select the product to be certified, including any variations, available interfaces, and relevant model information. They must also upload a Bill of Materials (BoM) file to the online portal. For security certification, the BoM must include the software version of the operating system, database, cryptography module, and any proprietary or third-party software used in the equipment. Upon submission of the application, the applicant will be informed of the applicable ITSAR and the associated fee.
Once the applicable fee is paid, the applicant must have their equipment tested against the relevant ITSAR by one of the designated TSTLs. The TSTL is responsible for completing the testing within 16 weeks, which includes any additional time required by the applicant to address any non-compliance issues discovered during testing. NCCS may assign a validator to oversee the technical aspects of the testing conducted at the TSTL.
Upon completion of testing, the TSTL will upload the test reports with the tested equipment's signature. A hard copy of the comprehensive test reports will also be provided to the NCCS unit. The test reports will be evaluated by the NCCS to determine compliance with the relevant ITSAR.
If the equipment is found to be compliant with the applicable ITSAR(s), a certificate will be issued to the applicant for the specific equipment model.
The certificate is typically issued within 4-8 weeks from the date of submission of complete test results, depending on the complexity of the equipment.
Note: If ITSAR is amended and a new version of the ITSAR released, it will be applicable from a prospective date indicated in the new version of ITSAR. Until that time, existing ITSAR will be applicable.