Standardization of charging ports
Electronic mobile devices have achieved worldwide adoption, but problems associated with them are also nearly as widespread. In 2020 alone, approximately 420 million portable electronic devices and mobile phones were sold in the EU. On average, consumers possess three mobile phone chargers, out of which they use two frequently. At the same time, 38% of consumers have encountered issues at least once, where they couldn't charge their mobile phones due to compatibility issues.
According to the Directive 2014/53/EU, amending Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU, all charging ports and fast charging technologies must be standardized by 2024 and will be mandated to acquire the CE marking which is required for goods sold in the European Economic Area (EEA).
This means that USB type-C will become the standard port across majority of the essential electronic devices. All USB connectors and USB cables are required to comply with IEC 62680-1-3 and all hosts, devices, hubs, chargers and cable assemblies with IEC 62680-1-2 for USB Power Delivery requirements.
These changes will be implemented by standardizing USB type-C ports (USB 3.0 & higher) across all handheld mobile phones, tablets, digital cameras, headphones, headsets, portable speakers, handheld video game consoles, e-readers, earbuds, keyboards, mice, and portable navigation systems as of 2024, and laptops as of 2026. This is because only USB type-C technology can support a power range of up to 240W, which will benefit both consumers and manufacturers alike.
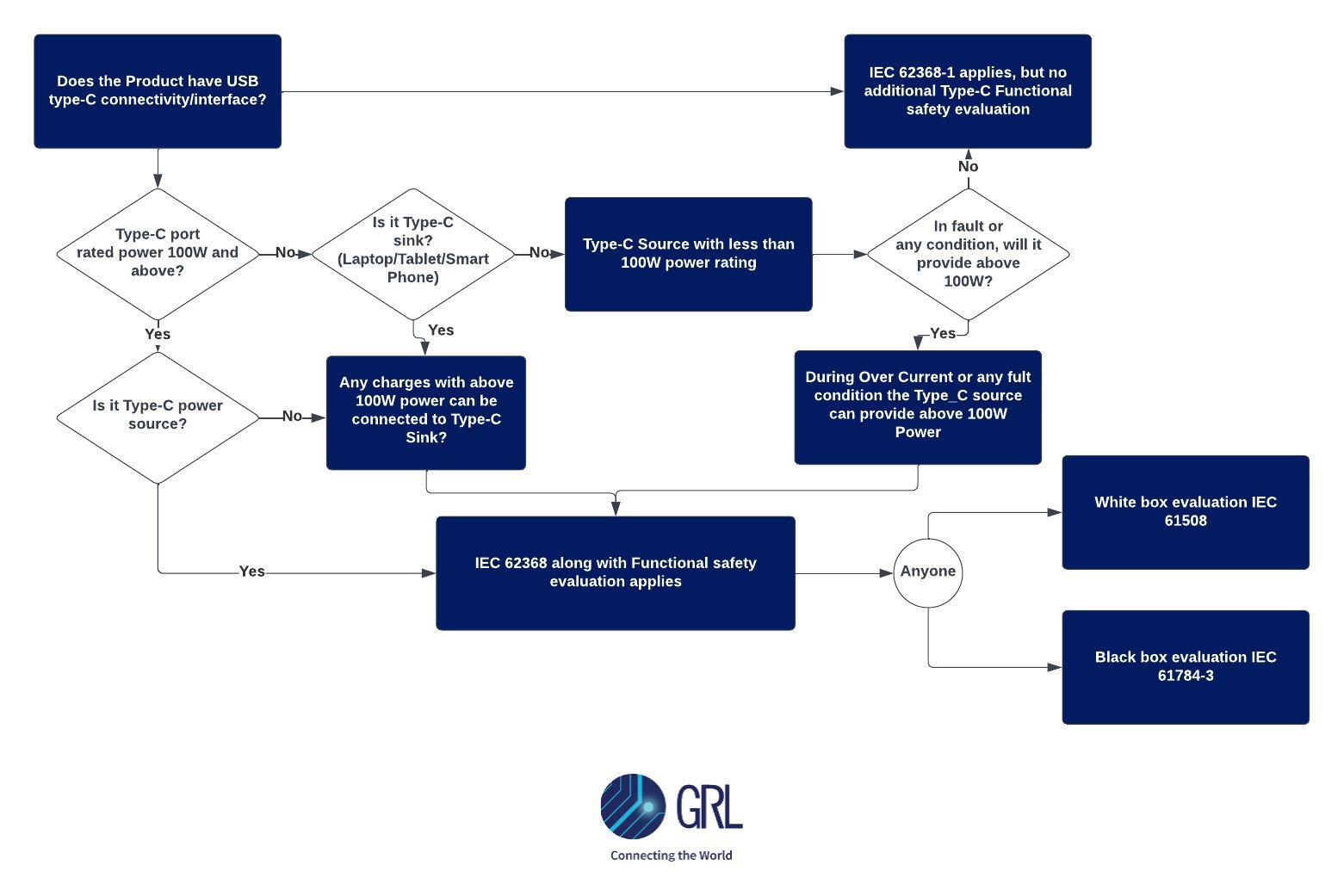
As Power Delivery charging rates increase and connectivity becomes more complex, there will be a higher chance of failures. So, it is important to have the components involved communicating amongst each other seamlessly. For cases where the cause of failure is unknown, the device should be able to fall back to a “risk addressed” state to avoid accidents, especially under high voltage conditions. This is particularly crucial for safety as the risk of fire tends to increase significantly at power levels above 100W USB ports. Ensuring Power Delivery functionality and electrical safety compliance according to IEC 62368-1 can be achieved by showing compliance to IEC 61784-3 functional safety requirements.
To build a mechanism that quickly communicates new charging standards to consumers and industry players, GRL has developed the C2-EPR, one of the few PD testers on the market designed to handle voltages greater than 100W and make compliance testing for IEC 61784-2 functional safety and IEC 62680-1-2 standards just a click away.
FAQ about various IEC standard series and certification processes
With a comprehensive suite of IEC testing services, manufacturers can comply with many other IEC standards such as IEC 63002, IEC 62680, IEC 61784-3 saving costs on the certification process while preparing themselves to launch products onto the market seamlessly.
What is the IEC?
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is a non-profit, non-governmental organization that develops and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. The organization introduced their very own IEC certification system in the 1930s, outlining the minimum performance and safety requirements of electrical and electronic products for mass consumption.
Over the years, the IEC has expanded its range of standards to cover topics such as electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, energy efficiency, and renewable energy.
Today, IEC certification is widely recognized and accepted by manufacturers, regulators, and consumers around the world. It has become an important tool for national government bodies to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical and electronic imports, and for promoting trade and commerce in these industries.
How does the IEC 62368-1 standard for communication technology work?
The IEC 62368-1 standard falls under the IEC certification umbrella and provides safety standards for audio, video, information, and communication technology equipment. Additionally, the standard serves as a framework for evaluating the safety of equipment that uses digital technology, including equipment that processes, stores, or communicates information. It replaces two earlier standards, IEC 60065 and IEC 60950, which were specific to audiovisual and information technology equipment, respectively.
Formulated based on the principles of hazard-based safety engineering, the IEC 62368-1 takes a risk-oriented approach to safety. This means that rather than specifying detailed technical requirements, the standard identifies potential hazards that manufacturers must avoid to demonstrate that equipment is safe.
By covering a wide range of equipment (computers, printers, telecommunications equipment, audio, video equipment, etc.) and safety features (electric shock, fire, and radiation, and includes requirements for insulation, grounding, temperature, etc.), the IEC 62368-1 standard provides a flexible and adaptable framework for ensuring the safety of modern digital equipment.
What does IEC 61784-3 standard for PROFIBUS communication profile mean?
IEC 61784-3 is a part of the IEC 61784 series (standards that define the communication networks and systems for industrial automation applications). Specifically, IEC 61784-3 which focuses on the communication profile for process control systems, known as PROFIBUS.
PROFIBUS is a widely used communication system in industrial automation that connects field devices such as sensors, actuators, and controllers. It allows for real-time communication between these devices and the control system, enabling precise control and monitoring of industrial processes.
The IEC 61784-3 defines the communication profile for PROFIBUS, specifying the physical layer, data link layer, and application layer protocols. It also provides guidelines for the implementation and maintenance of PROFIBUS networks, including recommendations for device configuration, diagnostics, and troubleshooting.
Therefore, the IEC 61784-3 plays an important role in ensuring interoperability and compatibility between PROFIBUS devices across different manufacturers, enabling seamless integration and communication in industrial automation systems.
How does the IEC 62680 standards series for USB work?
IEC 62680 is a series of standards for the specifications of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) communication protocol and connectors. The standard covers a wide range of USB applications, including data transfer, charging, and audio/video transmission. It is also crucial in ensuring the compatibility, safety, and reliability of USB connections in a wide range of applications, from charging mobile devices to transmitting audio and video signals.
IEC 62680 is divided into several parts, including:
- Common components of the USB protocol, such as electrical and physical specifications of USB connectors and cables.
- Design, construction, and testing of Micro-USB cables and connectors
- USB Power Delivery. Specifies the protocols for testing and delivering higher levels of power over USB connections safely to enable faster charge and higher-power application support.
- USB Type-C Authentication. Specifies the protocol for verifying the identity and authenticity of USB Type-C devices to guard against unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Visit our USB services page for more in-depth information on official USB compliance testing and logo certification programs.
Why do we need to comply with IEC standards?
Abiding by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards in various industries and applications provides manufacturers and distributors with a host of benefits, including:
Improved safety: IEC standards often provide guidelines for ensuring the safety of equipment, systems, and processes, helping to protect workers and consumers from potential hazards.
Increased efficiency: Standards can help to streamline processes and procedures, reducing waste, increasing productivity, and lowering costs.
Interoperability: Standards can ensure that products and systems from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly, improving compatibility and reducing the risk of errors or failures.
International recognition: IEC standards are widely recognized and accepted in many countries around the world, making it easier for companies to do business globally. Many national standards are based on IEC which makes it easier for manufacturers to show compliance.
Improved quality: Standards can help to ensure that products and systems meet specific quality criteria, leading to greater reliability and customer satisfaction.
Reduced risk: Standards can help to mitigate risks associated with new technologies or processes by providing guidelines and best practices for their safe and effective use.
