Granite River Labs, GRL
楊宗霖 Robert Yang
Release of Intel Core 13th gen processor
The laptop version of Intel Core™ 13th Gen Raptor Lake made its debut at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in January 2023. This follows the introduction of Raptor Lake-S desktop central processing units (CPUs) by Intel in September 2022. The Intel 13th gen launch also solidifies Intel’s impressive track record of new generation releases since the first “Intel Core” CPU family in 2006. What new experiences will the arrival of 13th gen Raptor Lake usher in for users? Let’s find out.
Intel 13th Gen CPU – Raptor Lake vs Alder Lake
Raptor Lake is widely regarded as an upgrade to the 12th generation Alder Lake, and maintains the architectural blueprint of its predecessor. Released in 2022, Alder Lake marked Intel’s first use of the "Intel 7 process" and "x86 hybrid architecture”, which 13th generation Raptor Lake builds upon by increasing core count (primarily E-Cores), expanding L2 cache memory, and raising clock speeds to ultimately enhance processor performance. This results in an impressive configuration of up to 8 P-Cores and 16 E-Cores, culminating in a total of 24 cores within flagship offerings.
The x86 hybrid architecture consists of the following two core types, with the CPU activating different cores based on various usage applications to achieve high efficiency and low power consumption:
- P-Core: Adopts the Golden Cove architecture which is suitable for high-performance and gaming applications.
- E-Core: Adopts the Gracemont architecture which is suitable for low-power and multitasking applications.
Figure 1: Key features of the 13th Gen Raptor Lake (source: Intel)
According to Intel, Raptor Lake improves upon Alder Lake’s core and overclocking capabilities while preserving the original socket configuration, allowing both manufacturers and consumers to enjoy a seamless upgrade pathway.
Specs and features of various Raptor Lake (RPL) processors
Raptor Lake-S series
Launched in late 2022, Raptor Lake-S is designed for desktop computers. Its flagship product, i9-13900K, features 24 cores (8 E-Cores, 16 P-Cores), 32 threads, and a maximum clock speed of 5.8GHz. It also has an increased L2 cache capacity, with 2MB for P-Cores and 4MB for E-Cores. According to Intel, the i9-13900K boasts up to 15% single-threaded and 41% multi-threaded performance improvements, offering significant performance strides compared to the previous generation i9-12900K.
Raptor Lake-P family (U/P/H)
Designed for laptops, the Raptor Lake-P family is the most widely-adopted processor family in the market. It consists of three series to cater for different power consumption profiles:
- RPL-U (15W): Prioritizing low power consumption, this series finds its place in ultra-lightweight models for users who value prolonged battery life and portability.
- RPL-P (28W): Striking a balance between energy efficiency and performance, this series is suitable for thin and light models, with slightly higher power consumption to offer sufficient performance for most business needs.
- RPL-H (45W): Packed with robust power and high performance, this series is usually paired with discrete graphics and used for gaming laptops.
Raptor Lake-HX series
Originally introduced with Alder Lake, the HX series stands at Intel’s highest consumer tier of laptop CPU offerings. This series empowers users with CPU overclocking capabilities, translating to desktop-level performance within the confines of laptops. Raptor Lake-HX is the market's first 24-core laptop CPU and it can reach a maximum clock speed of 5.6GHz. Its performance is on par with top-tier desktop CPUs, making it a formidable force in the realm of laptop gaming.
Raptor Lake mobile processors
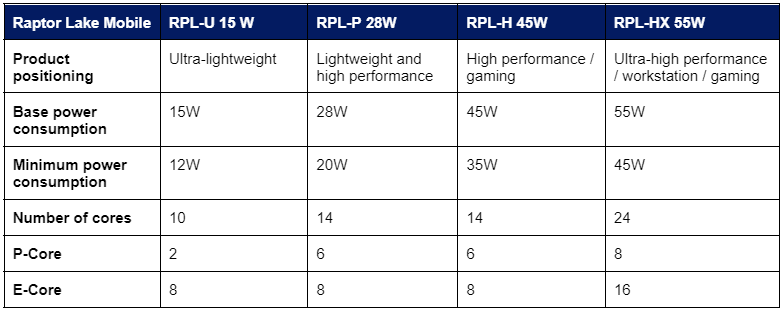
Table 1: Comparison of energy efficiency and performance levels across Raptor Lake mobile processors
Figure 2: Overview of the 13th Gen Intel Core Mobile Processors (source: Intel)
N-series processors
Alongside Raptor Lake, the Intel N-series processors also made their debut at the CES in early 2023. Tailored for lightweight laptops and small form factor computers, this lineup serves as a budget-friendly option that is suitable for educational institutions and cost-conscious users. The N-Series CPUs are equipped with either 4 or 8 sets of E-Cores and do not include P-Cores. Nevertheless, they support specifications such as DDR5 and LPDDR5 memory, as well as the USB Type-C™ Subsystem that enables both data and audiovisual transmission through the Type-C port. Despite its compact size, this series offers a robust range of features.
Figure 3: Overview of N-series features (source: Intel)
Updates on Thunderbolt (TBT) certification testing for Raptor Lake
Following the introduction of the 11th Gen CPU, Tiger Lake, Intel has been integrating Thunderbolt functionality directly into the CPU architecture. As a result, the Thunderbolt interface has evolved into a hallmark feature of Intel platforms, boasting impressive transmission speeds of up to 40 Gbps. But what sets apart the latest 13th Gen CPU in terms of Thunderbolt? Now, with the advent of the latest 13th Gen CPU, what distinct advancements can be observed in terms of Thunderbolt capabilities?
For laptops, while Raptor Lake processors inherently support TBT4, the product must have a retimer chip near the connector in order to also support TBT4. The retimer acts as a signal relay that is commonly used in high-speed signal transmission paths. It can be placed on the motherboard or in the cable to restore and amplify high-speed signals, thus compensating for any signal attenuation that might occur during transmission.
Within the Raptor Lake platform, manufacturers can choose between two retimer chips: the newly introduced Hayden Bridge (HBR) and the existing Burnside Bridge (BBR). The differences between the two are as follows:
Table 2: Differences between HBR and BBR retimers
From the above table, we can see that the HBR retimer supports higher USB 3.0 and DisplayPort™ (DP) specifications than the BBR retimer. This means electrical testing (EV) and functional testing (FV) for DP 2.1 and USB 3.2 Gen2x2 (20 Gbps) must be included in the TBT certification testing process for HBR. However, as there are currently no DP 2.1 monitor products available, FV testing for DP 2.1 can currently be omitted.
Here are the new features supported by Raptor Lake on the Thunderbolt port:
- USB 3.2 Gen2x2 (20 Gbps): As the next-generation technology within the USB 3.0 family, it adopts dual-channel transmission to double the transmission bandwidth compared to its predecessor, USB 3.2 Gen2x1 (10 Gbps). Several manufacturers have already released hard drive devices with this specification.
- DP 2.1: This is the latest specification for the DisplayPort (DP) interface. Compared to DP 1.4, which has 8.1 Gbps x 4 channels, DP 2.1 provides a maximum transmission speed of 20 Gbps x 4 channels (total bandwidth of 80 Gbps). It is expected to support resolutions up to 16K, delivering four times the high-definition quality of existing 8K monitors in the market. Additionally, DP 2.1 on the Raptor Lake platform supports two speeds: 10Gbps x 4Lane and 20Gbps x 4Lane. Both speeds will be covered during EV and FV testing. Currently, DP 2.1 is ready on the computer products (Display Source) and is awaiting the launch of monitor products (Display Sink).
The Past and Future of Intel Core CPUs
Figure 4: Roadmap of Intel core processor generations (source: Intel)
At present, the Intel Core line of processors has advanced to the 13th generation. Anticipations are set for the unveiling of the next-generation, Intel 4 process-based Meteor Lake by the end of 2023. Beyond Meteor Lake, Intel has announced plans to release generations of Intel Core processors that are packed with ever-increasing performance capabilities:
- NVL – Nova Lake (Gen 17) 2026
- LNL – Lunar Lake (Gen 16) 2025
- ARL – Arrow Lake (Gen 15) 2024
- MTL – Meteor Lake (Gen 14) 2023
- RPL – Raptor Lake (Gen 13) 2022
- ADL – Alder Lake (Gen 12) 2021
- TGL – Tiger Lake (Gen 11) 2020
Test your Thunderbolt™ products at GRL
As the first certification lab in the world qualified by Intel, we provide a complete range of testing services for Thunderbolt™. Backed by extensive experience in the certification and testing field, GRL excels in high-speed interface testing and has robust industry affiliations. You can rely on us to alleviate the challenges and complexities associated with product development.
Resources
https://www.intel.com.tw/content/www/tw/zh/gaming/resources/gaming-processor-names.html
https://today.line.me/tw/v2/article/aGr86Qo
https://www.pcworld.com/article/615644/intels-cpu-roadmap-now-extends-to-2024s-lunar-lake.html
Author
Robert Yang – Test Engineer, GRL (Taipei)
Robert has six years of testing experience and is familiar with the testing specifications for DisplayPort™, Thunderbolt, and HDMI®, USB. He is currently responsible for compatibility testing at GRL (Taipei) and helps customers solve problems and successfully obtain certification.


